
Solution: V 0 = 28 m/s, θ = 30 degrees (a) The maximum height = H max = ( V 0sinθ ) 2/(2 g) = (28 Sin 30)^2 / (2×9.8) m = 10 m (b) the time taken by the ball to return to the same level = Total time = T tot = 2(V 0sinθ )/g = (2x28xsin 30) /9.8 = 2.9 s (c) the distance from the thrower to the point where the ball returns to the same level = Horizontal range of a projectile = R = (V 0 2 sin2θ )/ g = (28x28xsin 60)/9. Most artillery games are based on the Projectile Motion Formula used to trace the trajectory of a projectile thrown in the air. The equations of the motion are applicable separately in X-Axis and the Y-Axis for finding the. n other words, its the acceleration due to gravity (g). In projectile motion, the only acceleration acting is in the direction and the direction is in the vertical direction. Calculate (a) the maximum height (b) the time taken by the ball to return to the same level (c) the distance from the thrower to the point where the ball returns to the same level. A projectile is an object that is in flight after we throw it or project it. Projectile Motion formula | equations of projectile motion Projectile Motion Solved ExampleĪ ball is thrown at a speed of 28 m/s in a direction 30 degrees above the horizontal. The initial velocity component along X-axis = V 0x = V 0 cosθ and the initial velocity component along Y-axis = V 0y = V 0sinθ.

The handy calculator tools available solve any type of problems easily as well as fastly.Figure 1: Projectile motion formula or equations We also published the most important Questions and Answers on Motion In A Plane MCQ For NEET with Answers. Physicscalc.Com is an advanced physics calculator tool where you can learn, practice, and discover various topics. Today we will cover the Simple Projectile Motion MCQs and Answers which covers terms like scalar product, inner product, vector product, triple scalar product, dot product and many other terms. So, calculate if he will be able to jump over the flames or not? Furthermore, he plans to take off from the ramp at a velocity of 9.0 m/s. Thus, the x component of the velocity remains constant at its initial value or vx v0x, and the x component of the acceleration is ax 0 m/s2. The ramp is inclined at an angle of 40° in relation to the water. Question: Suppose a water skier plans to set up a stunt in which he is going to jump over a burning obstacle. What are the time of flight equations We have exactly two equations for getting the flight time of a projectile motion. Vertical position = (horizontal osition) (tangent of launch angle) - / When a projectile is shot straight up in the air with only initial vertical speed and no horizontal speed, then its path follows the following projectile equation: h -16t2 +v0t + ho. If the projectile is thrown from a height, then use t V o sin() + ((V o sin())² + 2 g h)/g formula to obtain the flight time of the projectile.
The trajectory formula is mentioned-below:

The example of trajectory will br a ball thrown uwards, the path taken by the ball is determined by the gravity and resistance of air. Now, we can use the equations of motion for one dimension, i.e., v u + a t and s u t + 1 2 a t 2 for motion in the horizontal direction and also for motion of the projectile in vertical direction. In simple words, it is the curved path of an object under the gravity. Draw out the scenario so you can see how the object travels. (2) the object starts on the ground, soars through the air, and then lands on the ground some distance away from where it started.
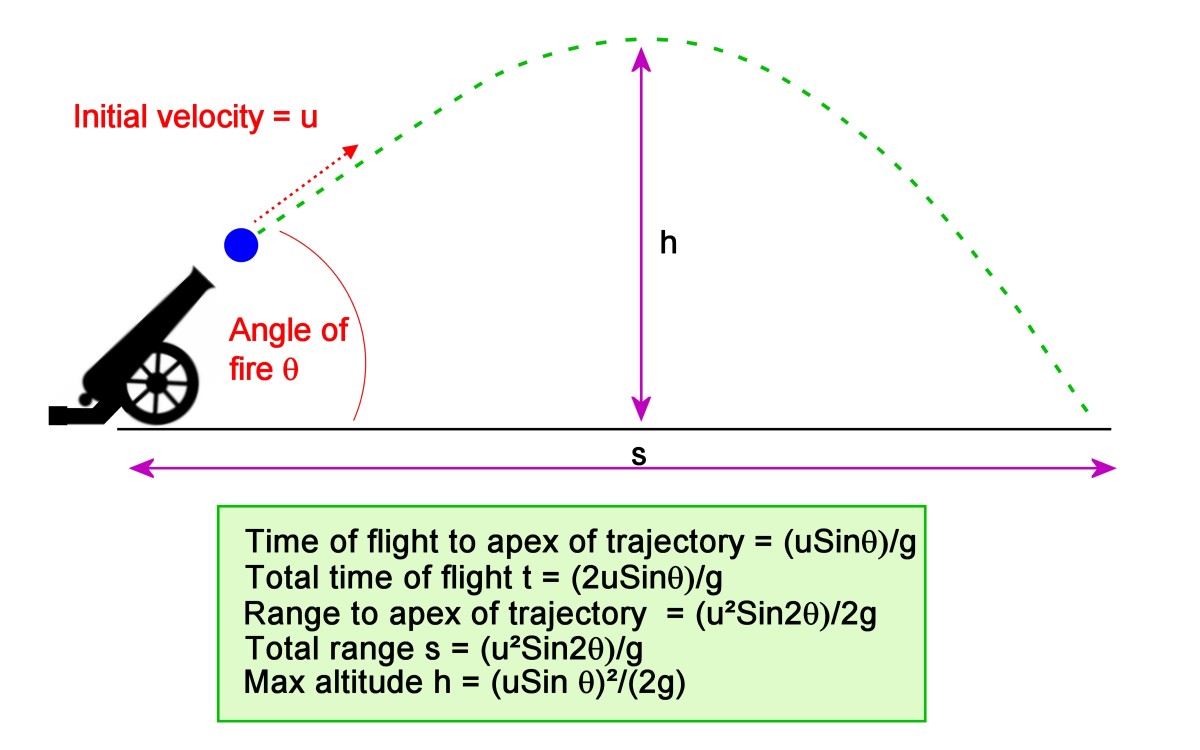
It can also be called as projectile motion. There are two types of projectile motion problems: (1) an object is thrown off a higher ground than what it will land on. The trajectory is the curved path of an object in relation with motion along with the gravity.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
